Best Foods for Sleep
Nutrition Guide for Better Rest
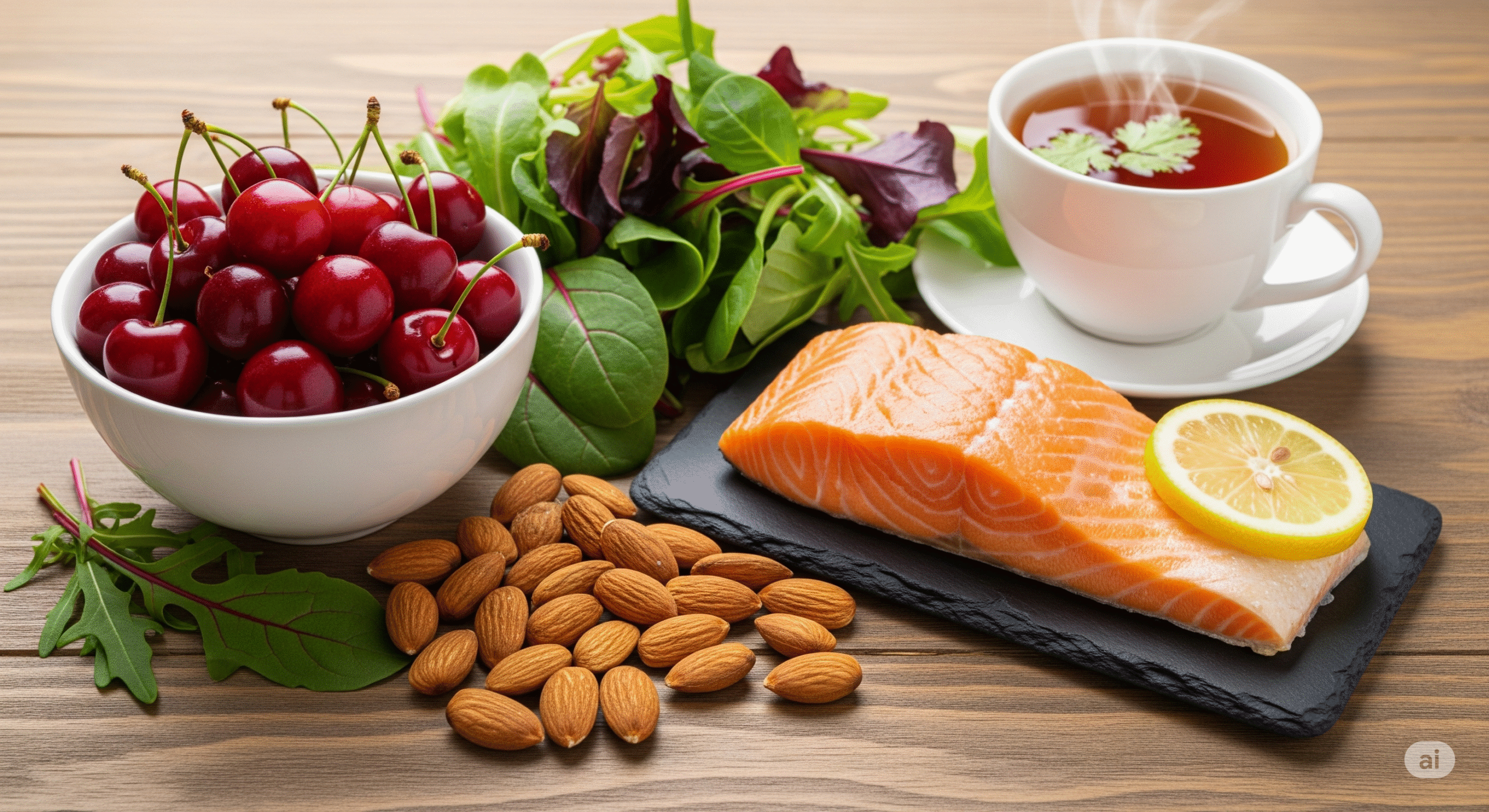

What if the key to your best night's sleep isn't found in your bedroom, but in your kitchen? The profound connection between nutrition and sleep quality is one of the most underestimated aspects of sleep optimization. Your dinner choice tonight could determine whether you sleep like a baby or toss and turn for hours, yet most people remain unaware of this powerful relationship. The science is clear: certain foods contain specific compounds that directly influence your body's production of sleep-regulating hormones and neurotransmitters, while others can sabotage your rest before you even hit the pillow. This comprehensive guide will explore the fascinating world of sleep nutrition, revealing how strategic food choices can naturally enhance your sleep quality, reduce the time it takes to fall asleep, and help you wake up feeling truly refreshed.
Debunking Nutrition and Sleep Myths
Before diving into the foods that can transform your sleep, it's essential to dispel common misconceptions that may be sabotaging your efforts to eat your way to better rest.
This oversimplified belief has led many people to go to bed hungry, which can actually impair sleep quality. The truth is more nuanced: timing and food type matter far more than the clock. Research shows that certain foods can actually promote sleep when consumed at the right time and in appropriate portions. The key is understanding which foods support sleep and avoiding those that hinder it, regardless of when you eat. A light, sleep-promoting snack 1-2 hours before bed can actually improve sleep onset and quality.
The demonization of carbohydrates has led to confusion about their role in sleep. While refined, high-sugar carbs can cause blood sugar spikes and crashes that disrupt sleep, complex carbohydrates can actually enhance sleep quality. Complex carbs increase the availability of tryptophan to the brain by triggering insulin release, which helps clear competing amino acids from the bloodstream. This allows more tryptophan to cross the blood-brain barrier and convert to serotonin and melatonin.
Perhaps one of the most dangerous sleep myths, the belief that alcohol is a sleep aid persists despite overwhelming scientific evidence to the contrary. While alcohol may initially make you feel drowsy and help you fall asleep faster, it significantly disrupts sleep architecture throughout the night. Alcohol suppresses REM sleep, increases sleep fragmentation, and can worsen sleep disorders like sleep apnea. The sleep you get after consuming alcohol is fragmented and less restorative.
This extreme approach ignores the fact that going to bed hungry can actually impair sleep quality. Low blood sugar during the night can trigger the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, causing you to wake up. Strategic, light snacking with sleep-promoting foods can actually enhance sleep quality and prevent middle-of-the-night awakenings.

Science-Backed Nutritional Strategies for Better Sleep
Understanding how specific nutrients and compounds affect your sleep physiology allows you to make informed choices that naturally enhance your rest. Here are the key nutritional strategies supported by scientific research.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that serves as the precursor to serotonin, which then converts to melatonin, your body's primary sleep hormone. However, simply eating tryptophan-rich foods isn't enough; you need to understand how to optimize its absorption and conversion.
Contains high levels of tryptophan, but the sleepiness after Thanksgiving dinner is more likely due to the large meal and carbohydrates consumed alongside it.
Particularly egg whites, which are rich in tryptophan and easily digestible. Perfect for a light evening snack.
Especially cottage cheese, which provides both tryptophan and casein protein for sustained amino acid release throughout the night.
Provides tryptophan plus omega-3 fatty acids that support brain health and sleep regulation.
Excellent plant-based source of tryptophan plus magnesium for enhanced relaxation effects.
Optimization tip: Combine tryptophan-rich foods with complex carbohydrates like oats, quinoa, or sweet potato for maximum sleep-promoting effect.
Magnesium is often called "nature's relaxant" due to its crucial role in muscle relaxation, nervous system function, and sleep regulation. Unfortunately, magnesium deficiency is common, affecting up to 50% of the population.
Provide magnesium plus healthy fats and protein. A small handful makes an ideal bedtime snack.
Spinach, Swiss chard, and kale are excellent sources of bioavailable magnesium.
Rich in magnesium and healthy monounsaturated fats that support overall health and sleep quality.
70% cacao or higher contains magnesium plus compounds that promote relaxation. Enjoy in moderation.
Provides magnesium plus complex carbohydrates for sustained energy and sleep support.
Optimization tip: Magnesium absorption is enhanced when consumed with vitamin D and can be impaired by excessive calcium intake at the same meal.

The right types of carbohydrates consumed at the right time can significantly improve sleep onset and quality by facilitating tryptophan transport to the brain.
Contain complex carbs plus natural melatonin and can be prepared as a warm, comforting bedtime snack.
Rich in complex carbs, potassium, and vitamin B6 (needed for serotonin production).
Contains GABA, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation, plus complex carbohydrates.
Simple and effective vehicle for tryptophan-rich toppings like almond butter or turkey.
Optimization tip: Consume complex carbohydrates 1-3 hours before bed for optimal effect without causing blood sugar spikes.
🥗 Optimize Your Sleep Nutrition
While whole foods should form the foundation of your sleep nutrition strategy, achieving optimal levels of sleep-promoting nutrients through diet alone can sometimes be challenging. Our research team has identified high-quality supplements that can fill nutritional gaps and accelerate your results.
Discover Sleep Nutrition Accelerators →*Clinically-studied nutrients for enhanced sleep quality
While your body naturally produces melatonin, certain foods contain this sleep hormone and can help boost your levels naturally.
One of the richest natural sources of melatonin. Tart cherry juice consumed 1-2 hours before bed has been shown to improve sleep quality.
Contain melatonin plus healthy omega-3 fatty acids that support brain health and sleep regulation.
Contains melatonin, vitamin C, and antioxidants that support sleep. Studies show eating 2 kiwis before bed improves sleep quality.
Particularly red grapes, contain melatonin and resveratrol, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties.
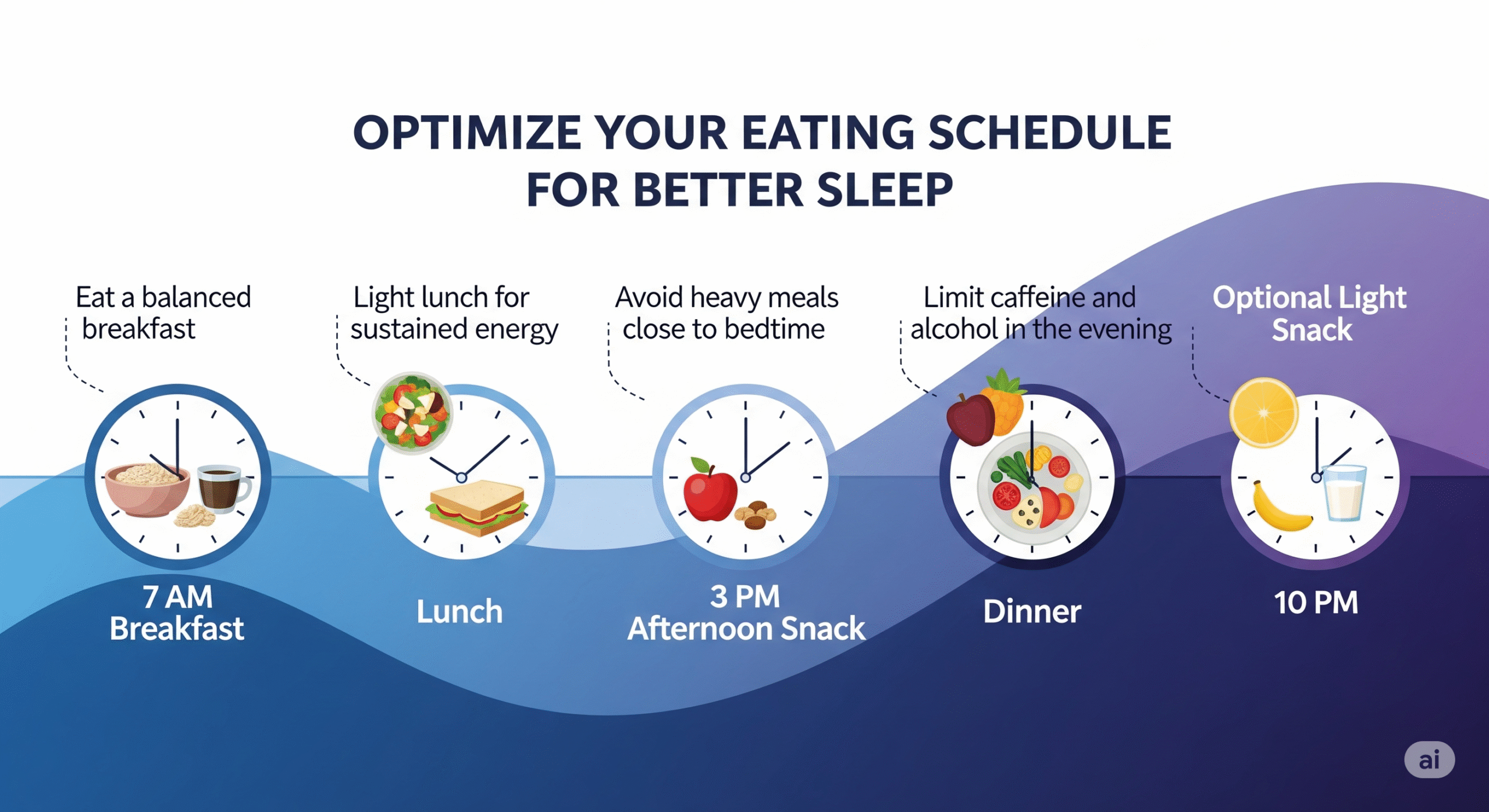
When and how you eat can be just as important as what you eat for optimal sleep quality.
Optimal Timing Strategies:
- Last large meal: 3-4 hours before bedtime to allow for proper digestion
- Light snack: 1-2 hours before bed if needed, focusing on sleep-promoting foods
- Hydration balance: Adequate fluids throughout the day but reduced intake 2 hours before bed to minimize nighttime awakenings
Ideal Macronutrient Ratios for Evening Meals:
- Moderate complex carbohydrates (40-50%): To facilitate tryptophan transport
- Lean protein (20-30%): Including tryptophan-rich sources
- Healthy fats (20-30%): To slow digestion and provide satiety
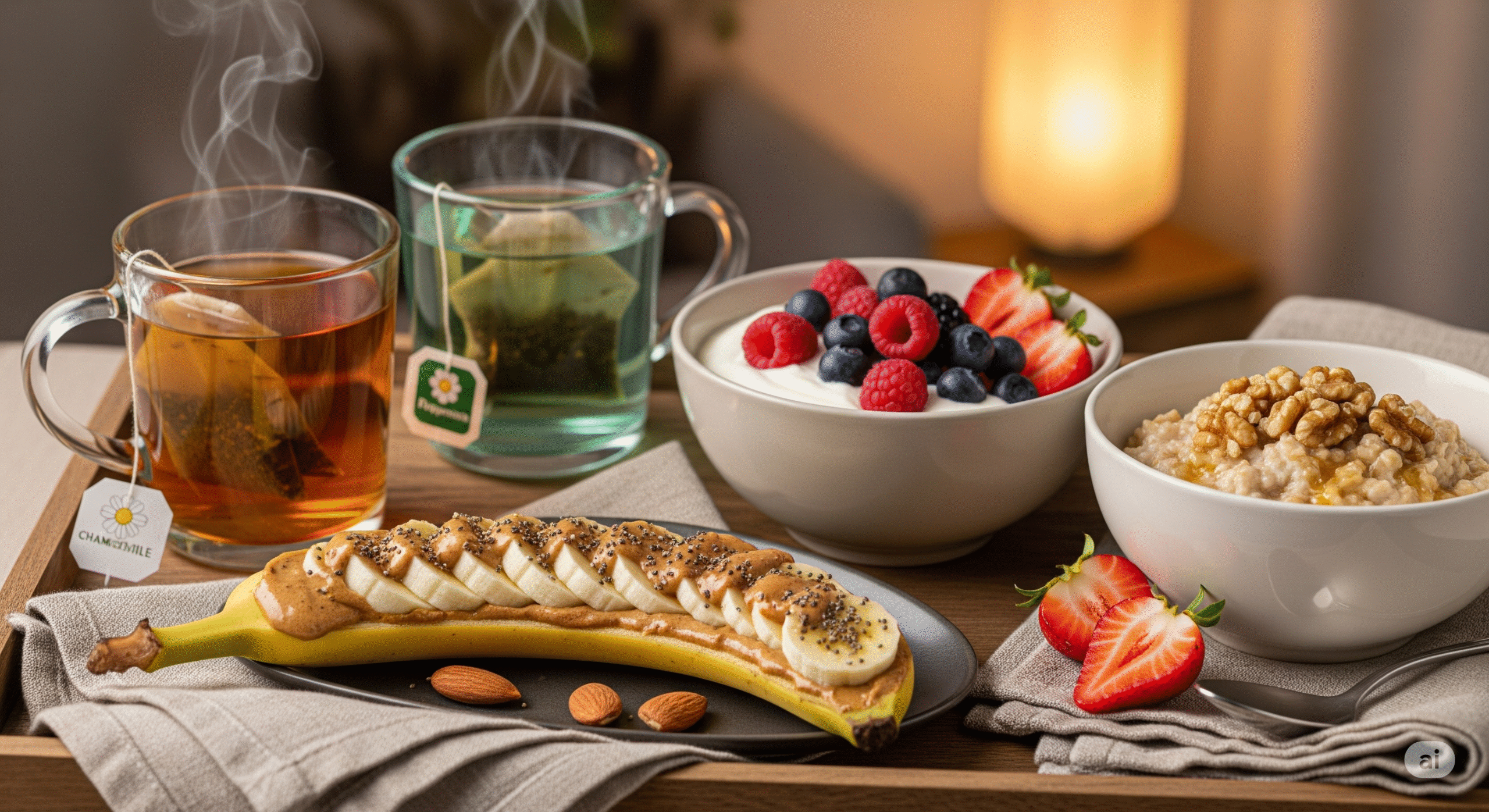
Functional Home Tips: Practical Sleep Nutrition Strategies
Beyond understanding the science, implementing practical strategies in your daily routine is key to experiencing the sleep benefits of optimal nutrition.
Ingredients: 1 banana, 1 tbsp almond butter, 1/4 cup oats, handful of spinach, 1 cup almond milk, 1 tsp honey
Instructions: Blend all ingredients until smooth. Consume 1-2 hours before bed for optimal sleep support.
Ingredients: 1/2 cup tart cherry juice, 1/2 cup Greek yogurt, 1 tbsp honey, 1/4 cup frozen cherries, ice cubes
Instructions: Blend until smooth and creamy. Rich in natural melatonin and protein for sustained sleep support.

Strategic Supplementation: Optimizing Your Sleep Nutrition
While whole foods should form the foundation of your sleep nutrition strategy, achieving optimal levels of sleep-promoting nutrients through diet alone can sometimes be challenging, especially in our modern food environment.
The Challenge of Nutrient Density
Modern agricultural practices, soil depletion, and food processing have reduced the nutrient density of many foods compared to previous generations. Additionally, individual absorption rates vary, and certain health conditions can impair nutrient uptake. This is where targeted, high-quality supplements can serve as valuable "accelerators" to ensure you're getting optimal levels of sleep-supporting nutrients.
Strategic Supplementation: Complementing Your Diet
While magnesium-rich foods are important, achieving therapeutic levels for sleep improvement often requires supplementation. Magnesium glycinate is highly absorbable and less likely to cause digestive upset than other forms.
While found in green tea, the amounts needed for significant sleep benefits typically require supplementation. L-Theanine promotes relaxation without drowsiness and can enhance the quality of sleep.
For those with disrupted circadian rhythms or age-related melatonin decline, supplementation can be more reliable than relying solely on food sources, which contain relatively small amounts.
🔬 Science-Backed Sleep Nutrition
Our recommended supplements are based on peer-reviewed research and clinical studies. We provide transparent information about optimal dosages, timing, and potential food interactions to help you make informed decisions about enhancing your sleep nutrition strategy.
View Research-Backed Formulations →Building Your Personal Sleep Nutrition Plan
The key to success with sleep nutrition is creating a sustainable plan that incorporates sleep-promoting foods while avoiding those that disrupt rest. Start by making small changes to your current diet, gradually incorporating more sleep-supportive foods and optimizing your meal timing.
Remember that consistency is key – the benefits of sleep-supportive nutrition compound over time as you establish healthy patterns and optimize your body's natural sleep processes. Consider targeted supplementation as a way to enhance your dietary efforts and ensure you're getting optimal levels of key nutrients.
Frequently Asked Questions
🍽️ Transform Your Sleep Through Nutrition
You now have the knowledge to optimize your sleep through strategic nutrition. Ready to accelerate your results with scientifically-proven supplements that complement your dietary efforts?
Get Your Sleep Nutrition Enhancement Kit →Join thousands who have transformed their sleep through nutrition
Scientific References
- St-Onge, M. P., Mikic, A., & Pietrolungo, C. E. (2016). Effects of diet on sleep quality. Advances in Nutrition, 7(5), 938-949.
- Wurtman, R. J., & Wurtman, J. J. (1995). Brain serotonin, carbohydrate-craving, obesity and depression. Obesity Research, 3(S4), 477S-480S.
- Roehrs, T., & Roth, T. (2001). Sleep, sleepiness, and alcohol use. Alcohol Research & Health, 25(2), 101-109.
- Kinsey, A. W., & Ormsbee, M. J. (2015). The health impact of nighttime eating: Old and new perspectives. Nutrients, 7(4), 2648-2662.
- Richard, D. M., Dawes, I. A., & Mathias, C. W. (2009). L-Tryptophan: Basic aspects in brain function. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 49(12), 1395-1404.
- Rosanoff, A., Weaver, C. M., & Rude, R. K. (2012). Suboptimal magnesium status in the United States: Are the health consequences underestimated? Nutrition Reviews, 70(3), 153-164.
- Abbasi, B., Kimiagar, M., Sadeghniiat, M. S., Shirazi, M. M., Hedayati, M., & Rashidkhani, B. (2012). The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 17(12), 1161.
- Afaghi, A., O'Connor, H., & Chow, C. M. (2007). High-glycemic-index carbohydrate meals shorten sleep onset. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 85(2), 426-430.
- Howatson, G., Bell, P. G., Tallent, J., Middleton, B., McHugh, M. P., & Ellis, J. (2012). Effect of tart cherry juice (Prunus cerasus) on melatonin levels and sleep quality. European Journal of Nutrition, 51(8), 909-916.
- Lin, H. H., Tsai, P. S., Fang, S. C., & Liu, J. F. (2011). Effect of kiwifruit consumption on sleep quality in adults with sleep problems. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 20(2), 169-174.
