10 Proven Relaxation Techniques
Master Your Mind-Body Connection

In our fast-paced, hyperconnected world, stress has become an unwelcome constant companion for millions. The statistics are alarming: chronic stress affects 77% of people regularly and is the number one cause of sleep disorders. But here's the remarkable truth that most people don't realize: just 10 minutes of targeted relaxation can reverse hours of stress damage to your nervous system. The relationship between stress and sleep is a vicious cycle where stress prevents quality sleep, and poor sleep amplifies stress, creating a downward spiral that affects every aspect of your health and well-being. However, this cycle can be broken with the right knowledge and techniques.
🔄 Breaking the Stress-Sleep Cycle
Stress → Poor Sleep → More Stress → Worse Sleep
The Solution: Proven relaxation techniques that interrupt this cycle and restore balance
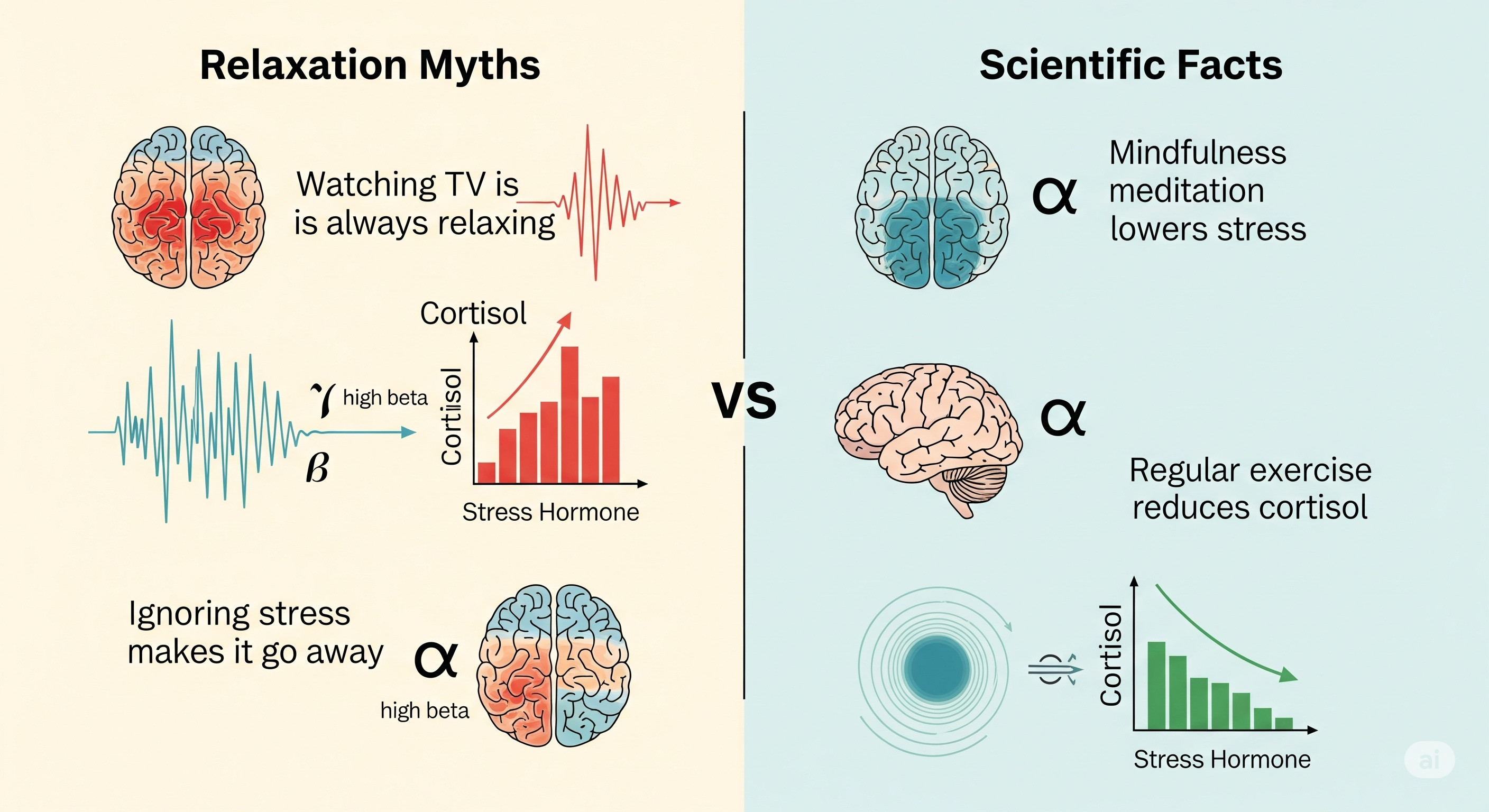
Debunking Relaxation and Meditation Myths
Before diving into effective techniques, it's crucial to dispel common misconceptions that often prevent people from experiencing the full benefits of relaxation practices.
This is perhaps the most pervasive and discouraging myth about meditation and relaxation. Many beginners become frustrated when they can't "turn off" their thoughts, believing they're failing at the practice. The scientific truth is that meditation and relaxation are not about eliminating thoughts but about changing your relationship with them. Research shows that the goal is to observe thoughts without judgment, allowing them to come and go naturally while gently returning your attention to your chosen focus point. Even experienced meditators have wandering minds; the practice lies in noticing when your mind has wandered and kindly bringing it back.
Many people avoid relaxation practices because they believe they require lengthy time commitments to be beneficial. However, scientific evidence demonstrates that even brief relaxation sessions can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, the body's "rest and digest" response, within minutes. Studies show that just 5-10 minutes of deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation can significantly reduce cortisol levels and activate the relaxation response. While longer sessions may provide deeper benefits, even short practices can be remarkably effective for stress reduction and sleep preparation.
This catch-22 thinking prevents many stressed individuals from beginning relaxation practices when they need them most. The reality is that relaxation techniques are specifically designed to work regardless of your starting emotional state. In fact, they're most valuable when you're feeling anxious, stressed, or agitated. Research demonstrates that these practices can effectively shift your nervous system from a state of sympathetic arousal (fight-or-flight) to parasympathetic dominance (rest-and-digest) even when you begin feeling highly stressed.
10 Science-Backed Relaxation Techniques
The following techniques are supported by extensive scientific research and have been proven effective for reducing stress, lowering cortisol levels, and improving sleep quality. Each technique works through different mechanisms, allowing you to find the approaches that resonate most with your lifestyle and preferences.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation is a systematic technique that involves tensing and then releasing different muscle groups throughout your body. This practice helps you become aware of physical tension and learn to consciously release it.
How it works:
PMR activates the parasympathetic nervous system and has been shown to significantly reduce cortisol levels, blood pressure, and anxiety while improving sleep quality. The contrast between tension and relaxation helps you recognize and release chronic muscle tension you may not even realize you're carrying.
Step-by-step guide:
- Find a comfortable position lying down or sitting in a supportive chair
- Close your eyes and take three deep breaths
- Starting with your toes, tense the muscles for 5-7 seconds, then release and relax for 15-20 seconds
- Notice the contrast between tension and relaxation
- Move systematically through your body: feet, calves, thighs, buttocks, abdomen, hands, arms, shoulders, neck, and face
- End with a full-body tension for 5 seconds, then complete relaxation
- Remain in this relaxed state for several minutes, breathing naturally
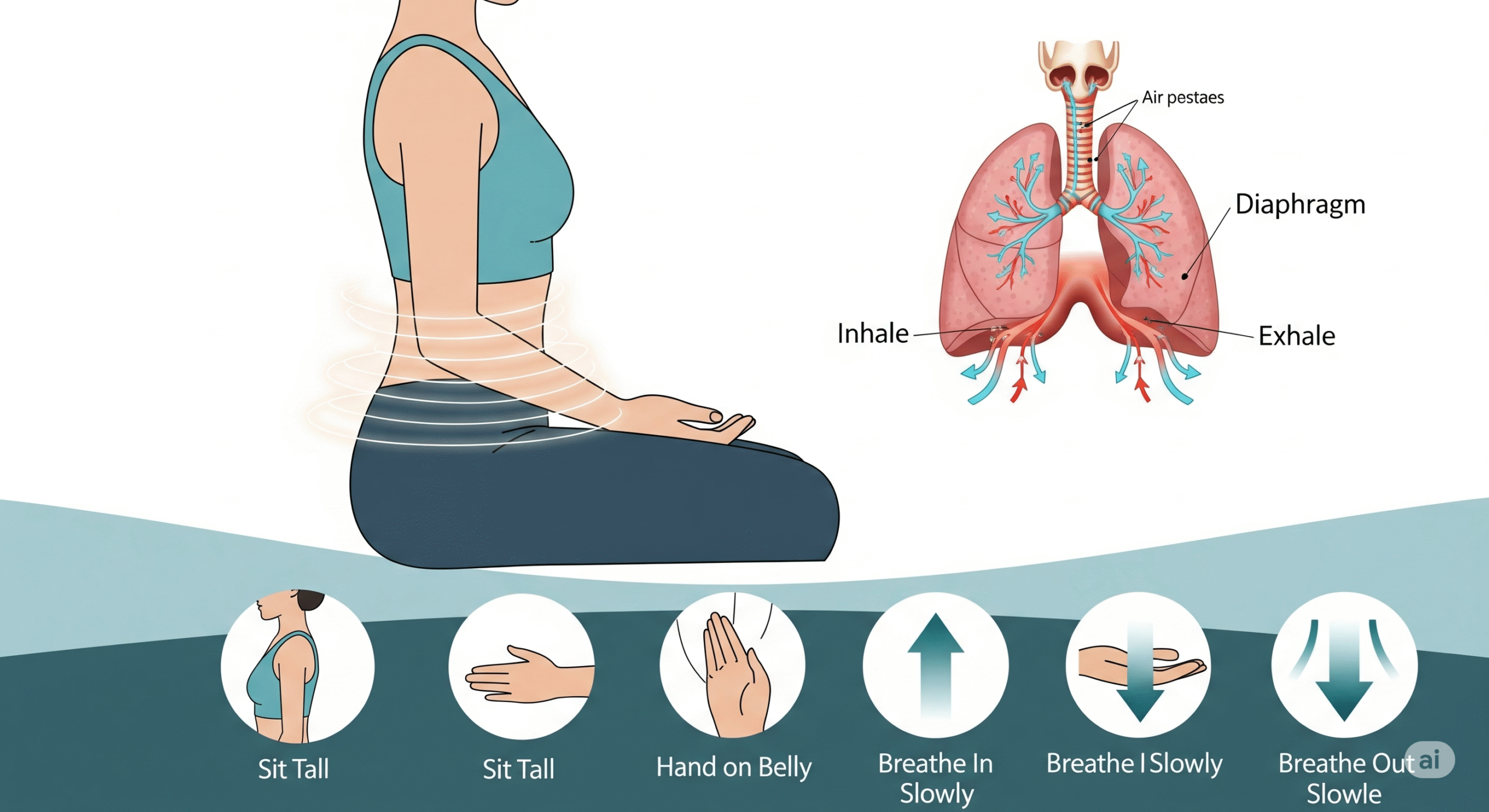
The 4-7-8 breathing technique, popularized by Dr. Andrew Weil, is a simple yet powerful method for activating the vagus nerve and inducing rapid relaxation.
How it works:
This breathing pattern stimulates the vagus nerve, which triggers the parasympathetic nervous system and promotes a state of calm. The extended exhale helps remove carbon dioxide from the lungs and slows the heart rate. Research shows it can reduce anxiety and improve sleep onset within minutes of practice.
Step-by-step guide:
- Sit or lie in a comfortable position with your back straight
- Place the tip of your tongue against the ridge behind your upper front teeth
- Exhale completely through your mouth, making a whoosh sound
- Close your mouth and inhale quietly through your nose for 4 counts
- Hold your breath for 7 counts
- Exhale completely through your mouth for 8 counts, making the whoosh sound
- Repeat the cycle 3-4 times initially, gradually building up to 8 cycles
Mindfulness meditation involves focusing your attention on the present moment, typically by observing your breath, bodily sensations, or thoughts without judgment.
How it works:
Regular mindfulness practice has been shown to reduce activity in the default mode network of the brain, which is associated with rumination and anxiety. Studies demonstrate that mindfulness meditation can improve sleep quality, reduce insomnia symptoms, and lower stress hormones.
Simple practices for beginners:
- Breath awareness: Sit comfortably and focus on your natural breathing. When your mind wanders, gently return attention to your breath
- Body scan: Systematically focus on different parts of your body, noticing sensations without trying to change them
- Loving-kindness: Direct feelings of goodwill toward yourself and others, starting with the phrase "May I be happy, may I be peaceful"
Guided imagery involves using your imagination to create calming, peaceful mental scenes that promote relaxation and stress relief.
How it works:
Visualization activates the same neural pathways as actual experiences, allowing your nervous system to respond to imagined peaceful scenarios as if they were real. Research shows that guided imagery can reduce cortisol levels, lower blood pressure, and improve sleep quality.
Effective visualization techniques:
- Beach scene: Imagine yourself on a peaceful beach, feeling warm sand, hearing gentle waves, and feeling a cool breeze
- Forest walk: Visualize walking through a serene forest, noticing the sounds of birds, the smell of pine, and dappled sunlight
- Mountain meadow: Picture yourself in a beautiful meadow surrounded by mountains, feeling completely safe and peaceful
Body scan meditation involves systematically focusing your attention on different parts of your body, promoting awareness and relaxation.
How it works:
This practice helps you develop interoceptive awareness (awareness of internal bodily signals) and can identify areas of tension you might not consciously notice. Research shows that body scan meditation can reduce chronic pain, improve sleep, and decrease anxiety.
Step-by-step guide:
- Lie down comfortably with your eyes closed
- Begin by focusing on your breath for a few minutes
- Direct your attention to the top of your head, noticing any sensations
- Slowly move your attention down through your body: forehead, eyes, jaw, neck, shoulders, arms, chest, abdomen, hips, thighs, knees, calves, and feet
- Spend 30-60 seconds on each body part, simply observing without trying to change anything
- If you notice tension, breathe into that area and allow it to soften naturally
- End by focusing on your body as a whole
🌿 Enhance Your Relaxation Response
While these natural techniques are powerful, many people find that targeted supplements can amplify their relaxation response and help achieve deeper states of calm more quickly. Our research team has identified natural compounds that work synergistically with these practices.
Discover Natural Relaxation Enhancers →*Scientifically-backed ingredients for enhanced stress relief
Also known as "yogic sleep," this practice guides you through a state of conscious relaxation between waking and sleeping, promoting deep rest and stress relief.
A self-hypnosis technique that uses verbal cues to induce relaxation by focusing on physical sensations like warmth and heaviness in different body parts.
These gentle, flowing movement practices combine meditation, breathing, and slow movements to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Using electronic monitoring to gain awareness and control over physiological functions like heart rate and muscle tension to achieve relaxation.
Using specific frequencies, nature sounds, or music to induce relaxation and reduce stress through auditory stimulation of the nervous system.

Functional Home Tips: Creating Your Relaxation Sanctuary
Beyond formal techniques, numerous practical strategies can help you create an environment and lifestyle that naturally promotes relaxation and better sleep.
The Role of Natural Relaxation Aids
While these natural relaxation techniques form the foundation of stress management and better sleep, some individuals may benefit from additional support to optimize their relaxation response and achieve faster, more consistent results.
Certain natural compounds can enhance your body's ability to relax and transition into restorative sleep. These aren't replacements for the techniques you've learned, but rather "accelerators" that can work synergistically with your relaxation practices.
Key Natural Relaxation Compounds:
- L-Theanine: This amino acid, found naturally in green tea, promotes relaxation without drowsiness by increasing alpha brain waves associated with calm alertness. Research shows it can enhance the effectiveness of meditation and relaxation practices.
- Magnesium: Often called "nature's relaxant," magnesium plays a crucial role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including those that regulate the nervous system. Magnesium deficiency is common and can contribute to anxiety and sleep problems.
- Ashwagandha: This adaptogenic herb has been used for centuries to help the body manage stress. Modern research confirms its ability to reduce cortisol levels and improve sleep quality.
🔬 Science-Backed Relaxation Support
Our recommended natural compounds are backed by peer-reviewed research and clinical studies. We provide transparent information about dosages, timing, and potential interactions, ensuring you can make informed decisions about incorporating these natural aids into your routine.
View Research-Backed Formulations →Building Your Personal Relaxation Toolkit
The key to success with relaxation techniques is finding the methods that work best for you and practicing them consistently. Start with one or two techniques that resonate with you, practice them regularly for at least a week, and then gradually expand your toolkit.
Remember that relaxation is a skill that improves with practice. Be patient with yourself, especially in the beginning. Even if your mind wanders or you don't feel immediately relaxed, you're still benefiting from the practice. The goal is progress, not perfection.
Frequently Asked Questions
🎯 Master Your Stress Response
You now have a comprehensive toolkit of relaxation techniques. Ready to enhance your results with natural compounds that support your body's relaxation response?
Get Your Relaxation Enhancement Kit →Join thousands who have mastered stress-free living
Scientific References
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Stress in America: A National Mental Health Crisis. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2020/report-october
- Goleman, D., & Davidson, R. J. (2017). Altered Traits: Science Reveals How Meditation Changes Your Mind, Brain, and Body. Avery.
- Zaccaro, A., Piarulli, A., Laurino, M., Garbella, E., Menicucci, D., Neri, B., & Gemignani, A. (2018). How breath-control can change your life: A systematic review on psycho-physiological correlates of slow breathing. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 12, 353.
- Pascoe, M. C., Thompson, D. R., & Ski, C. F. (2017). Yoga, mindfulness-based stress reduction and stress-related physiological measures: A meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 86, 152-168.
- Riegel, B., & Gory, B. (2016). Progressive muscle relaxation: A systematic review. Journal of Holistic Nursing, 34(3), 253-264.
- Weil, A. (2015). The 4-7-8 Breath: A Natural Tranquilizer for the Nervous System. Retrieved from https://www.drweil.com/videos-photos/videos/breathing-exercises-4-7-8-breath/
- Rusch, H. L., Rosario, S. R., Levison, L. M., Olivera, A., Harrison, C., Hartley, N. A., ... & Wolever, R. Q. (2019). The effect of mindfulness meditation on sleep quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1445(1), 5-16.
- Menzies, V., Taylor, A. G., & Bourguignon, C. (2006). Effects of guided imagery on outcomes of pain, functional status, and self-efficacy in persons diagnosed with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 12(1), 23-30.
- Ditto, B., Eclache, M., & Goldman, N. (2006). Short-term autonomic and cardiovascular effects of mindfulness body scan meditation. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 32(3), 227-234.
- Hidderley, M., & Holt, M. (2004). A pilot randomized trial assessing the effects of autogenic training in early stage cancer patients in relation to psychological status and immune system responses. European Journal of Oncology Nursing, 8(1), 61-65.

Wagner P
Natural Health Researcher & Founder of LabOfficial
Wagner is dedicated to researching and testing safe, natural solutions for everyday health problems. Through LabOfficial, he shares effective home remedies and recommends science-backed supplements that simplify healing and restore well-being without side effects.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified health professional before starting any new diet, exercise program, or supplementation.